What is GIS Software used for?
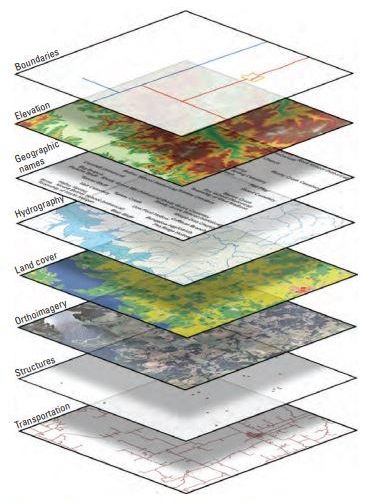
Geographic Information System (GIS) software is a tool that enables users to visualize, analyze and interpret data that has a spatial component. This software uses maps, satellite imagery, and aerial photographs to create, manage, and analyze geospatial information.
Today, countless organizations use GIS like Maptive to create maps that effectively convey information, conduct analyses, exchange data, and tackle intricate global issues. As a result, the utilization of GIS is revolutionizing how the world operates. But what does this mean in practice?
Mapping and Spatial Analysis
GIS software is essential for mapping and spatial analysis, providing powerful tools to create and manipulate geospatial data. GIS software manages and analyzes geospatial data represented by points, lines, and polygons on a map.
Analysts, experts and ordinary people use GIS software in various industries for mapping and spatial analysis. For example, in the insurance industry, GIS software maps and analyzes risks associated with natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods.
Environmental Management
Another application of GIS is environmental management. Environmental management is the process of managing the impact of human practices on the environment. It involves identifying and mitigating environmental risks, reducing pollution, and conserving natural resources. Environmental management is critical for businesses and industries that want to reduce environmental impact.
GIS software is an essential tool for environmental management. It provides tools for managing and analyzing geospatial data, allowing experts the data they need to identify and mitigate environmental risks. GIS software can help businesses and industries track and monitor environmental data, identify areas of environmental concern, and develop strategies to reduce their environmental impact.
Urban Planning and Development
A third area that you will notice GIS software is in urban planning and development, what most people know as the process of designing, managing and developing cities and urban areas to improve livability and sustainability. It involves various activities, including land use planning, transportation planning, housing development, and infrastructure planning.
In this industry, GIS software is essential for helping urban planning experts analyze land use patterns, identify areas with high levels of traffic congestion, and develop transportation plans to improve traffic flow, for more efficient communities.
Retail
In the retail industry, location is crucial in driving business success. Leading retailers recognize this and leverage mapping and location analytics to make informed decisions about business expansion, customer behavior, and asset management, such as inventory and supply chain networks. Using GIS technology, analysts can create web-based maps, infographics, and analyses to provide colleagues across the enterprise with insights into performance and operations.
Health and Medical Services
Professionals in health and human services are reaping the benefits of utilizing the valuable insights that location-based data offers. By leveraging spatial data and GIS technology, they can identify areas lacking coverage among the populations they aim to serve, optimize workflow processes, and plan for and manage unforeseen events—the application of GIS results in better health outcomes and greater access to healthcare.
In Governments
National governments utilize GIS technology to oversee programs and assess the effectiveness of policies. Through GIS, agency staff and leaders can integrate various data sources to develop a comprehensive understanding of issues, implement practical solutions, share key insights, and foster engagement with stakeholders and the general public.
Conclusion
GIS software has become essential for various industries, including environmental management, urban planning and development and natural resource management, to name a few. With the continued growth of geospatial data and the increasing demand for more accurate and comprehensive spatial analysis, the prospects for GIS software are bright.
Thus, many users of GIS believe the future of the software will likely involve integrating more advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, real-time data analysis and machine learning. The intent is that users can process and analyze larger quantities of geospatial data quickly and accurately, improving decision-making processes and enhancing operational efficiency.
839GYLCCC1992



Leave a Reply